AI is Changing the World: Real-World Examples
Curious about how artificial intelligence is being used today? This listicle provides 7 compelling AI use case examples demonstrating practical applications across various industries. Discover how AI is revolutionizing everything from healthcare and finance to manufacturing and transportation. These AI use case examples provide insights into the exciting ways AI is shaping our future, offering inspiration for hobbyists, marketers, and anyone interested in the power of AI.
1. Healthcare Diagnostics and Treatment Planning
AI is rapidly transforming healthcare, and one of the most promising ai use case examples lies in diagnostics and treatment planning. By leveraging the power of machine learning and deep learning, AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data – from medical images like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to patient records and even genomic data – to assist doctors in making more accurate and efficient diagnoses. These systems can identify subtle patterns and anomalies that might be missed by the human eye, potentially leading to earlier disease detection and more personalized treatment protocols. This approach helps streamline the diagnostic process, enabling doctors to focus more on patient care and less on time-consuming data analysis.
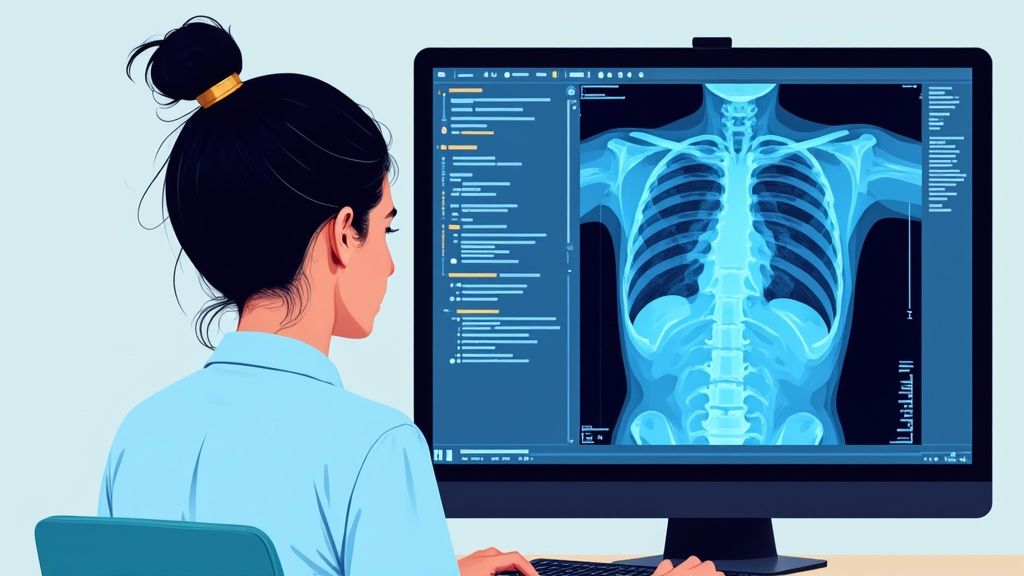
This area of AI application boasts several key features, including medical image analysis, natural language processing for deciphering medical records, predictive analytics for forecasting disease progression, and genomic data interpretation for personalized medicine. Imagine a future where your doctor can predict your risk of developing a particular disease based on your genetic makeup and lifestyle factors, and then tailor a preventative plan specifically for you. That’s the potential of AI in healthcare. Real-time patient monitoring and alerts add another layer of improvement, allowing for proactive interventions and potentially life-saving responses.
Successful implementations of AI in healthcare diagnostics are already making a difference. Google DeepMind's AI system boasts a remarkable 94% accuracy in detecting eye diseases, while IBM Watson for Oncology analyzes cancer treatment options, offering valuable insights to oncologists. PathAI uses machine learning to enhance the accuracy of pathology diagnoses, and Aidoc's FDA-cleared AI system flags acute conditions in CT scans, helping radiologists prioritize critical cases. Zebra Medical Vision also contributes with its AI algorithms that detect various conditions from medical imaging.
Pros:
- Earlier and more accurate disease detection: Catch diseases in their early stages when treatment is often most effective.
- Reduced diagnostic errors: Minimize human error and improve diagnostic accuracy.
- Personalized treatment recommendations: Tailor treatment plans to individual patients based on their unique characteristics.
- Time savings for healthcare professionals: Free up doctors’ time so they can focus on patient interaction and complex cases.
- Improved patient outcomes through precision medicine: Deliver more effective and targeted treatments, leading to better health outcomes.
Cons:
- Potential algorithmic bias: AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on, and biased data can lead to inaccurate or discriminatory results.
- Privacy and security concerns: Protecting sensitive patient data is paramount.
- Regulatory hurdles: Navigating the regulatory landscape for AI medical systems can be challenging.
- Lack of explainability: Understanding how some AI systems arrive at their conclusions can be difficult.
- High implementation costs: Integrating AI into existing healthcare systems can be expensive.
Tips for Implementation:
- Validate on diverse populations: Ensure AI systems are tested and validated on diverse patient populations to minimize bias.
- Assistive tool, not replacement: Use AI as a tool to assist clinicians, not replace their expertise.
- Address data privacy: Prioritize data privacy and security from the outset.
- Train healthcare professionals: Educate healthcare providers on how to interpret and use AI recommendations effectively.
- Establish clear protocols: Define when human judgment should override AI suggestions.
This use case deserves a top spot on our list because it exemplifies the transformative power of AI. It has the potential to revolutionize how we diagnose and treat diseases, ultimately leading to longer, healthier lives. While challenges remain, the potential benefits of AI in healthcare are undeniable, and ongoing advancements promise even more exciting developments in the future.
2. Financial Fraud Detection and Risk Assessment
One of the most impactful AI use case examples today is in the realm of financial fraud detection and risk assessment. This technology empowers financial institutions to identify and prevent fraudulent activities in real-time, protecting both businesses and consumers. AI systems continuously analyze vast amounts of financial data, looking for subtle patterns and anomalies that indicate potentially fraudulent transactions. This goes beyond simply checking if a transaction amount exceeds a certain limit; these systems are sophisticated enough to understand individual customer behavior, flagging unusual spending patterns or login attempts from unexpected locations. This proactive approach allows financial institutions to stop fraud before it occurs, minimizing financial losses and enhancing customer trust. Beyond fraud detection, AI also plays a crucial role in assessing creditworthiness, leading to more accurate lending decisions.

This method works by leveraging several key AI capabilities: real-time transaction monitoring, behavioral biometrics for user authentication, anomaly detection algorithms, network analysis to identify fraud rings, adaptive learning from new fraud patterns, and credit risk scoring models. Features like behavioral biometrics analyze how a user interacts with their device – typing speed, scrolling habits, etc. – adding another layer of security beyond traditional passwords. Network analysis allows AI to connect seemingly disparate fraudulent activities and uncover organized fraud rings. And adaptive learning ensures the system constantly evolves to stay ahead of emerging fraud tactics.
Examples of successful implementation abound. Mastercard's Decision Intelligence technology, for instance, has reportedly reduced false declines by 50%, improving the customer experience significantly. PayPal utilizes a robust AI-powered fraud prevention system that processes over $100 billion in payments annually. FICO's Falcon Fraud Manager is a trusted solution used by over 9,000 financial institutions globally, demonstrating the widespread adoption of this technology. Other major players like Capital One and JPMorgan Chase also utilize AI extensively for fraud detection and risk management. Learn more about Financial Fraud Detection and Risk Assessment for additional insights.
When and why should you consider this approach? If your business handles financial transactions or manages credit risk, AI-powered fraud detection and risk assessment are essential. The benefits are numerous: reduced financial losses, lower false positives, 24/7 monitoring, the ability to detect novel fraud patterns, more accurate risk assessment, and an improved customer experience.
Pros:
- Reduced financial losses from fraud
- Lower false positives compared to rule-based systems
- 24/7 monitoring without human fatigue
- Ability to detect novel fraud patterns
- More accurate risk assessment for lending
- Improved customer experience with fewer false declines
Cons:
- Initial investment in AI infrastructure
- Requirement for large, high-quality datasets
- Need for continuous model updates as fraud tactics evolve
- Potential for adversarial attacks on AI systems
- Regulatory compliance challenges
Tips for Implementation:
- Use a hybrid approach combining rules-based and ML systems.
- Implement explainable AI features for regulatory compliance.
- Ensure real-time processing capabilities for immediate fraud prevention.
- Maintain human oversight for complex cases.
- Regularly retrain models with new data to prevent concept drift.
This item deserves its place on the list of AI use case examples because it represents a powerful application of AI with tangible, real-world benefits. It tackles a critical challenge faced by businesses and consumers alike, leveraging the power of AI to create a safer and more secure financial landscape. Popularized by companies like Visa, Mastercard, PayPal, FICO, Feedzai, and Darktrace, AI-driven fraud detection and risk assessment is not just a trend, but a fundamental shift in how we manage financial security.
3. Intelligent Customer Service and Support
In today's fast-paced world, customers expect quick, efficient, and personalized support around the clock. This is where AI-powered customer service solutions shine as a prime ai use case example. By leveraging natural language processing (NLP), sentiment analysis, and machine learning, businesses can provide automated support through various channels like chatbots, virtual assistants, and intelligent ticket routing systems. These technologies enable 24/7 customer engagement, personalized responses, and efficient resolution of common issues, freeing up human agents to tackle more complex problems.

Imagine a chatbot instantly answering a customer's question about their order status at 3 AM or a virtual assistant guiding them through a troubleshooting process. This is the power of AI in customer service. Features like natural language understanding and generation allow these systems to comprehend and respond to customer queries in a conversational manner. Sentiment analysis adds another layer of intelligence, enabling the system to detect customer emotions and tailor responses accordingly. For example, if a customer expresses frustration, the AI can escalate the issue to a human agent or offer a more empathetic response. Automated ticket classification and routing further streamline the support process, ensuring that inquiries reach the appropriate agent quickly. All of this contributes to a more efficient and satisfying customer experience.
Learn more about Intelligent Customer Service and Support
Several companies have already witnessed the transformative impact of AI-powered customer service. Zendesk's Answer Bot, for example, resolves up to 30% of customer tickets automatically, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues. Similarly, Intercom's Resolution Bot addresses common customer questions, while Bank of America's virtual assistant, Erica, has handled over 50 million client requests. Even in brick-and-mortar settings, AI is making a difference. Lowe's LoweBot helps customers navigate stores and find products, while Sephora's beauty bot provides personalized product recommendations. These real-world ai use case examples demonstrate the tangible benefits of incorporating AI into customer service strategies. AI is driving significant changes in how businesses interact with their customers. Implementing effective digital transformation strategies for customer service is crucial for staying competitive and meeting evolving customer expectations. As more businesses embrace these technologies, we can expect even more innovative applications of AI in customer service.
Pros:
- 24/7 availability for customer support
- Reduced wait times for customers
- Lower operational costs for support centers
- Consistent service quality across interactions
- Scalability during peak demand periods
- Data collection for service improvement
Cons:
- Limited handling of complex or nuanced issues
- Potential customer frustration with obvious AI interactions
- Training requirements for effective implementation
- Integration challenges with existing CRM systems
- Ongoing maintenance to improve response accuracy
Tips for Implementation:
- Start with automating common, straightforward queries.
- Create clear escalation paths to human agents for complex issues.
- Use customer feedback to continuously improve AI responses.
- Maintain a conversational, natural-sounding tone for chatbot interactions.
- Be transparent about when customers are interacting with AI.
- Implement analytics to track resolution rates and customer satisfaction.
This approach is particularly valuable for businesses experiencing high volumes of customer inquiries, those operating in a 24/7 environment, or those seeking to improve customer satisfaction and reduce support costs. By intelligently automating routine tasks, businesses can free up their human agents to focus on more complex issues and provide a more personalized and efficient customer experience.
4. Manufacturing Process Optimization and Predictive Maintenance
In the world of manufacturing, efficiency is king. Downtime is costly, and even small improvements in productivity can have a massive impact on the bottom line. This is where AI steps in as a game-changer, offering powerful solutions for optimizing processes and predicting maintenance needs. This AI use case example focuses on how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing factory floors, transforming traditional manufacturing into smart, data-driven operations.
So, what exactly does AI-powered manufacturing optimization entail? Essentially, AI systems analyze vast quantities of data gathered from various sources across the manufacturing environment. This includes data streaming from IoT sensors embedded in equipment, production line performance data, and even environmental factors. By applying machine learning algorithms, these systems can identify patterns, detect anomalies, and make predictions about future performance. Think of it as giving your factory a brain that can learn and adapt in real-time.
How does it work?
Imagine a network of sensors monitoring the vibrations and temperature of a critical machine on the assembly line. The AI system continuously analyzes this data, comparing it to historical performance and established thresholds. When the system detects an anomaly, such as unusual vibrations, it can predict a potential failure before it occurs. This allows maintenance teams to schedule repairs proactively, minimizing costly unplanned downtime and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Features that drive this transformation:
- IoT sensor data integration and analysis: The foundation of this approach lies in collecting real-time data from connected sensors.
- Anomaly detection for equipment performance: AI algorithms identify unusual patterns that indicate potential problems.
- Predictive maintenance scheduling algorithms: These algorithms forecast when maintenance should be performed to prevent failures.
- Digital twin simulations of machinery: Virtual models of physical equipment allow for testing and optimization in a risk-free environment.
- Process optimization for yield improvement: AI can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the production process.
- Quality control vision systems: AI-powered cameras can detect defects and ensure consistent product quality.
Real-world success stories abound:
- Siemens implemented AI at its Amberg electronics plant, resulting in a remarkable 25% reduction in defects.
- General Electric's Predix platform uses AI to monitor turbine performance, predicting maintenance needs and optimizing efficiency.
- BMW leverages AI for quality control in its vehicle production, ensuring high standards and minimizing errors.
- Intel's predictive maintenance program, powered by AI, has reportedly saved them a staggering $100 million in manufacturing costs.
- Bosch utilizes machine learning for process optimization across its 280 plants globally.
Pros and Cons:
While the benefits are significant, it's important to be aware of the challenges:
Pros:
- Reduced unplanned downtime (typically 30-50%)
- Extended equipment lifespan
- Lower maintenance costs
- Optimized inventory for spare parts
- Improved product quality and consistency
- Energy consumption reduction
Cons:
- High initial investment in sensors and infrastructure
- Data integration challenges with legacy equipment
- Need for specialized AI expertise
- Cultural resistance in traditional manufacturing settings
- Cybersecurity vulnerabilities in connected systems
Tips for successful implementation:
- Start with high-value use cases that provide quick ROI.
- Ensure robust data collection from critical equipment.
- Develop clear metrics to measure AI implementation success.
- Train maintenance teams to work alongside AI systems.
- Implement gradual changes to avoid disrupting production.
- Create feedback loops for continuous improvement.
This AI use case example deserves its place on the list because it represents a significant step towards Industry 4.0, the fourth industrial revolution. By leveraging AI, manufacturers can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, productivity, and cost savings. Learn more about Manufacturing Process Optimization and Predictive Maintenance. For non-technical AI enthusiasts and hobbyist vibe builders interested in how AI can transform go-to-market strategies and workflow automations (including prompting LLMs in tools like Replit, n8n, and Zapier), this example provides a concrete illustration of AI's practical power. Popular platforms like Siemens MindSphere, GE Digital, PTC ThingWorx, IBM Maximo, Microsoft Azure IoT, and Uptake are driving the adoption of these technologies.
5. Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization
One of the most impactful ai use case examples is the transformation of supply chain and logistics. AI applications are revolutionizing how goods move and are managed, optimizing everything from inventory levels and demand forecasting to route planning and warehouse operations. These intelligent systems analyze massive datasets – encompassing historical sales data, weather patterns, economic indicators, and real-time transportation conditions – to create highly efficient and resilient supply chains. This leads to significant cost reductions while simultaneously improving delivery performance, a win-win for businesses and consumers alike.
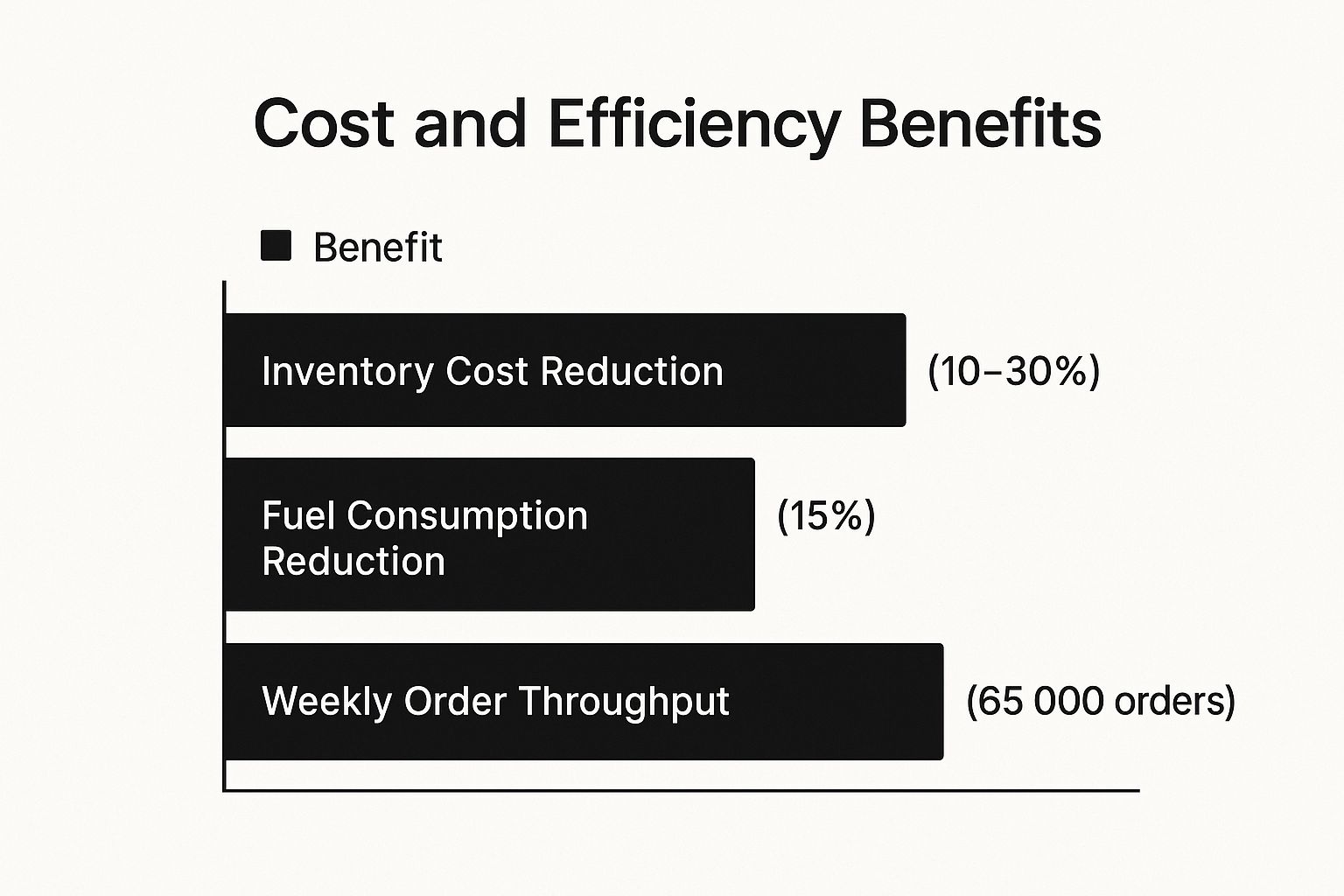
The infographic above visualizes key data related to the impact of AI on supply chain key performance indicators (KPIs). It demonstrates how AI-driven optimization can lead to significant improvements across various areas. For instance, the chart highlights a potential 10-30% reduction in inventory holding costs, a crucial metric for any business. Furthermore, it shows improvements in on-time delivery and order fulfillment rates, directly impacting customer satisfaction. The visualization also emphasizes the potential for reduced transportation costs and improved supply chain visibility, leading to a more streamlined and cost-effective operation.
Features like demand forecasting with multiple variables, inventory optimization algorithms, dynamic route optimization, and automated warehouse operations with robotics are powering this change. AI also plays a crucial role in supplier risk assessment and provides real-time shipment tracking with accurate ETA predictions. Think about how this level of optimization can impact everything from the availability of your favorite products to the speed at which they arrive at your doorstep.
This approach offers numerous advantages, including reduced inventory holding costs (typically 10-30%), improved order fulfillment rates, lower transportation costs, and enhanced supply chain visibility. It also builds better resilience against disruptions and allows for optimized workforce allocation. For instance, Amazon’s inventory forecasting has reportedly reduced storage costs by billions, while Walmart uses AI to optimize food freshness throughout its supply chain. DHL leverages AI for route optimization, reducing fuel consumption by 15%, and Ocado's automated warehouse systems process a staggering 65,000 orders weekly. Maersk, a global leader in container shipping, utilizes predictive analytics to further optimize its complex logistics operations. These examples demonstrate the real-world impact and effectiveness of AI in supply chain management.
However, implementing AI in supply chain management isn't without its challenges. Data quality and integration can be significant hurdles, and implementation across multiple partners can be complex. Algorithms require continuous updates, and finding the right balance between automation and human judgment is crucial. Initial transition periods may also cause temporary disruptions.
So, when and why should you consider this approach? If you're looking to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency and customer satisfaction within your supply chain, AI-powered optimization is a game-changer. Learn more about Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization for a deeper dive into this topic.
Here are some actionable tips for successful implementation:
- Focus on data quality: Clean, accurate, and integrated data is the foundation of effective AI.
- Start small: Begin with well-defined problems like demand forecasting before tackling more complex areas.
- Collaboration is key: Ensure buy-in from all stakeholders across the supply chain.
- Manage the change: Implement change management processes alongside AI adoption to smooth the transition.
- Flexibility is essential: Build in flexibility to handle unexpected exceptions and disruptions.
- Visualize your progress: Create dashboard visualizations for key metrics to track performance and identify areas for improvement.
Companies like Amazon, Blue Yonder (formerly JDA Software), Manhattan Associates, IBM Sterling Supply Chain, o9 Solutions, and Llamasoft are leading the charge in popularizing AI-driven supply chain solutions. This signifies the growing importance and adoption of this transformative technology. This ai use case example deserves its place on this list due to its potential for widespread impact and tangible benefits across various industries.
6. Personalized Marketing and Recommendation Systems
This AI use case example demonstrates the power of personalization in the digital age. Personalized Marketing and Recommendation Systems leverage AI to analyze vast amounts of data, transforming how businesses interact with their customers. These intelligent systems sift through user behavior, stated preferences, and even contextual information like time of day and location to deliver highly targeted marketing content, product suggestions, and content recommendations. This is a prime example of an AI use case that enhances both the customer experience and a business's bottom line.
How it Works:
At the heart of these systems are sophisticated algorithms. Collaborative filtering identifies users with similar tastes and recommends items they've enjoyed. Content-based recommendations analyze the characteristics of items a user likes and suggest similar ones. Real-time personalization engines take things a step further, dynamically adjusting recommendations based on immediate user actions. This level of granularity ensures that the most relevant options are presented to each individual user at the optimal moment.
Examples of Success:
The effectiveness of personalized recommendations is evident in some of the world's most successful companies. Think about Netflix, where a whopping 80% of content watched stems from its recommendation system. Amazon, another giant, sees 35% of its sales generated through AI-powered product recommendations. Even Spotify's Discover Weekly, a beloved feature for music lovers, uses AI to curate personalized playlists. These examples highlight how AI-driven personalization can significantly impact user engagement and drive business growth.
Why This AI Use Case Matters:
In today's crowded digital landscape, grabbing and retaining customer attention is paramount. Personalized Marketing and Recommendation Systems offer a powerful solution. By delivering relevant content and offers, businesses can significantly boost conversion rates (often by 10-30%), increase average order values, and foster stronger customer loyalty. This approach also reduces marketing waste by eliminating irrelevant targeting, ensuring that marketing budgets are used efficiently. For vibe builders and those focused on go-to-market strategies, this AI use case can be a game-changer, allowing for hyper-personalized campaigns that resonate deeply with target audiences. This particular application of AI is invaluable for anyone exploring AI for workflow automations, as it streamlines the process of delivering the right message to the right person at the right time.
Pros:
- Increased conversion rates (typically 10-30%)
- Higher average order values
- Improved customer retention and loyalty
- Reduced marketing waste on irrelevant targeting
- Enhanced user experience through relevance
- Scalable personalization across millions of users
Cons:
- Privacy concerns and regulatory compliance challenges
- Recommendation filter bubbles limiting discovery
- Cold start problem for new users or products
- Need for extensive data collection
- Computational resource requirements for real-time systems
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Balance personalization with privacy: Be transparent with users about how their data is being used.
- Gather diverse feedback: Implement both implicit (behavior-based) and explicit (user-provided) feedback mechanisms.
- Promote discovery: Include diversity in recommendations to avoid filter bubbles and introduce users to new items.
- Start simple: Begin with basic recommendation techniques before implementing more complex algorithms.
- Test and measure: A/B test recommendations against control groups to gauge their effectiveness.
- Consider context: Factor in contextual elements like time, location, and device for even more relevant recommendations.
Learn more about Personalized Marketing and Recommendation Systems (Note: this link seems to be about AI creative tools, not personalized recommendations, so it might need to be updated to a more relevant resource.)
This AI use case exemplifies how AI can be used to enhance the customer journey and drive business outcomes. By leveraging these powerful techniques, businesses can create more meaningful interactions, foster stronger relationships, and ultimately, thrive in the competitive digital marketplace. Companies like Netflix, Amazon, Spotify, YouTube, Pinterest, Adobe Experience Platform, and Salesforce Einstein have popularized and proven the effectiveness of AI-driven personalization. Whether you're a hobbyist vibe builder or exploring AI use cases for Replit, n8n, or Zapier, understanding and implementing personalized marketing and recommendation systems is key to maximizing engagement and achieving your goals.
7. Autonomous Vehicles and Transportation
Self-driving cars, robotaxis, and autonomous delivery bots aren't science fiction anymore—they're powered by AI, and this is one of the most exciting ai use case examples currently in development. This transformative technology is revolutionizing how we move people and goods, offering the potential for safer, more efficient, and accessible transportation systems. At the heart of autonomous vehicles and transportation systems is Artificial Intelligence.
This technology works by equipping vehicles with a suite of sensors, including cameras, lidar (light detection and ranging), radar, and ultrasonic sensors, to perceive their surroundings. This "perception system" feeds data into powerful AI algorithms that use techniques like computer vision, sensor fusion, and deep learning. These algorithms then interpret the data, identify objects (pedestrians, other vehicles, traffic lights), and make real-time driving decisions such as steering, accelerating, and braking. Beyond individual vehicles, AI also optimizes traffic flow in smart cities, predicting congestion and dynamically adjusting traffic signals.
Features that make it work:
- Perception Systems: Cameras, lidar, radar, and ultrasonic sensors create a 360-degree view of the vehicle's environment.
- Object Detection and Classification: AI algorithms identify and categorize objects in real-time, differentiating between pedestrians, cyclists, cars, and other obstacles.
- Path Planning and Decision Making: AI determines the optimal route and makes driving decisions based on the perceived environment and traffic conditions.
- Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) Communication: Vehicles share information about their speed, location, and intentions, improving safety and coordination.
- Predictive Modeling of Traffic Patterns: AI analyzes historical and real-time data to anticipate traffic congestion and optimize traffic flow.
- End-to-End Learning for Driving Behavior: AI models learn directly from human driving data, improving their ability to handle complex scenarios.
Why Autonomous Vehicles Deserve a Spot on this List: This technology has the potential to drastically reshape our world. Think fewer accidents, less traffic, and increased mobility for everyone, including the elderly and disabled. It’s a prime example of how AI can solve real-world problems.
Real-World Success Stories:
- Waymo: Offering autonomous taxi services in Phoenix, Arizona, showcasing the viability of self-driving technology in a real-world setting.
- Tesla: Autopilot and Full Self-Driving features demonstrate the increasing integration of AI-powered driving assistance in consumer vehicles.
- Cruise: Operating self-driving vehicles in San Francisco, pushing the boundaries of autonomous navigation in complex urban environments.
- Nuro: Using autonomous delivery vehicles for last-mile logistics, illustrating the potential of AI to transform industries beyond personal transportation. Think pizza delivered by a robot!
- Mobileye: Provides Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) leveraging AI-powered features like lane keeping assist and adaptive cruise control in over 100 million vehicles worldwide.
Pros:
- Safety: Reduced accidents and fatalities due to the elimination of human error.
- Accessibility: Increased mobility for individuals who cannot drive.
- Efficiency: Optimized traffic flow and reduced congestion.
- Sustainability: Lower emissions through efficient driving.
- Productivity: Repurposed commuting time for work or leisure.
- Cost Reduction: Lower transportation costs for goods delivery.
Cons:
- Regulation and Liability: Unclear legal frameworks for accidents involving autonomous vehicles.
- Cost: High development and implementation expenses.
- Public Trust: Overcoming public hesitation and building trust in the technology.
- Edge Cases: Handling unpredictable and unusual situations.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting autonomous systems from hacking and malicious attacks.
- Job Displacement: Potential job losses for professional drivers.
Tips for Development and Implementation:
- Redundancy: Implement backup systems for critical functions to ensure safety.
- Data Collection: Gather data from diverse driving environments to train robust AI models.
- Ethical Frameworks: Establish clear guidelines for decision-making in unavoidable accident scenarios.
- Gradual Adoption: Integrate autonomous vehicles gradually alongside human-driven vehicles.
- Cybersecurity: Prioritize cybersecurity from the initial design phase.
- Transparent Communication: Clearly communicate the capabilities and limitations of the technology to the public.
This application of AI isn't just about making cars drive themselves; it's about creating a future where transportation is safer, more efficient, and accessible to all. It's a compelling example of how AI is being used to address complex challenges and transform our everyday lives.
7 AI Use Cases Comparative Overview
| Use Case | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Diagnostics and Treatment Planning | High – requires integration with medical devices, regulatory approval | High – specialized data, secure infrastructure, expert training | Improved diagnostic accuracy, personalized treatment, early disease detection | Hospitals, clinics, precision medicine initiatives | Reduced errors, time savings, better patient outcomes |
| Financial Fraud Detection and Risk Assessment | Medium-High – continuous model updates, integration with banking systems | High – large quality datasets, high-performance real-time processing | Reduced fraud losses, accurate risk assessment, real-time alerts | Banks, payment processors, credit risk management | 24/7 monitoring, detects new fraud patterns, fewer false positives |
| Intelligent Customer Service and Support | Medium – NLU models, CRM integration, ongoing training | Medium – conversational AI, multi-language support, analytics | 24/7 responsiveness, reduced wait times, scalable support | Customer support centers, help desks, ecommerce platforms | Lower costs, consistent service, improved scalability |
| Manufacturing Process Optimization and Predictive Maintenance | High – IoT integration, sensor deployment, legacy system compatibility | High – sensors, data platforms, AI expertise | Reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, improved quality | Factories, production plants, heavy machinery operations | Increased equipment lifespan, energy savings, defect reduction |
| Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization | High – multi-partner data integration, dynamic algorithms | High – data pipelines, optimization software, change management | Cost reductions, better delivery, improved resilience | Retailers, distributors, logistics companies | Inventory cost savings, fuel reduction, enhanced visibility |
| Personalized Marketing and Recommendation Systems | Medium – advanced algorithms, real-time personalization engines | Medium-High – user data, computing power, data privacy compliance | Higher conversion rates, increased retention, marketing efficiency | Ecommerce, streaming services, digital marketing | Scalable personalization, improved user engagement |
| Autonomous Vehicles and Transportation | Very High – sensor fusion, complex environment perception, safety certification | Very High – expensive hardware, simulation/testing infrastructure | Safer roads, reduced congestion, increased accessibility | Automotive, public transit, logistics & delivery | Accident reduction, optimized traffic, cost savings |
The Future of AI: Limitless Potential
From revolutionizing healthcare diagnostics to powering self-driving cars, the AI use case examples we've explored demonstrate the remarkable impact artificial intelligence is having on our world. Key takeaways include the potential for increased efficiency, improved accuracy, and personalized experiences across various sectors. Whether it's optimizing manufacturing processes, detecting financial fraud, or enhancing customer service, AI is transforming how we live and work. Mastering an understanding of these core AI applications is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the future landscape of business and technology. By embracing the potential of AI, we can unlock unprecedented opportunities for innovation and solve some of the world's most pressing challenges. These AI use case examples are just the beginning. As AI technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more groundbreaking applications to emerge, reshaping industries and enhancing our lives in ways we can only imagine.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of AI and connect with fellow enthusiasts? VibeMakers is the perfect platform to explore AI use case examples, discover new trends, and collaborate on cutting-edge projects. Join the VibeMakers community today and be a part of the AI revolution!