AI: Reshaping the Business Landscape
Want to see how artificial intelligence is making waves in business? This list dives into 7 practical AI in business examples, showing how it's impacting everything from customer service to fraud detection. Discover how AI can boost efficiency, personalize marketing, and even predict future trends. Whether you're a hobbyist vibe builder, exploring AI for go-to-market strategies, or just curious about AI workflow automation, this list provides clear, concise examples of AI in action.
1. Customer Service AI Chatbots
Customer service AI chatbots are transforming how businesses interact with their customers. These intelligent virtual assistants leverage natural language processing (NLP) to understand and respond to customer inquiries, providing support and information around the clock. They act as a first line of defense, handling common questions, resolving simple issues, and escalating complex problems to human agents when necessary. This allows businesses to offer seamless and efficient customer service while freeing up human agents to focus on more demanding tasks. As an example of AI in business, chatbots showcase the power of automation and intelligent communication.

These chatbots are packed with features designed to enhance the customer experience and streamline operations. NLP capabilities allow them to understand the nuances of human language, while 24/7 availability ensures customers receive instant responses, regardless of time zone. Progressive learning allows the chatbot to improve its performance over time by learning from past interactions. Many platforms offer multilingual support, catering to a global customer base. Seamless integration with existing business systems like CRM platforms ensures a unified customer experience. Sentiment analysis capabilities allow the chatbot to detect customer emotions and tailor its responses accordingly.
The benefits of implementing AI chatbots are numerous. They can reduce customer service operational costs by up to 30% by handling a large volume of inquiries simultaneously. This leads to consistent service quality across all interactions. Chatbots also collect valuable customer data and insights, providing businesses with valuable information to improve their products and services. Learn more about Customer Service AI Chatbots for deeper insights.
However, like any technology, AI chatbots have limitations. They may struggle with complex or nuanced requests that require human intervention. Poorly implemented chatbots can frustrate customers, leading to negative experiences. Regular updates and maintenance are necessary to ensure optimal performance, and the initial setup costs can be significant. Privacy and data security are also important considerations.
Numerous companies have successfully implemented AI chatbots to enhance their customer service. Bank of America's Erica has handled over 100 million client requests since its launch, demonstrating the scalability and efficiency of this technology. H&M's chatbot assists customers in finding products and completing purchases, while Sephora's chatbot provides personalized beauty recommendations. Mastercard's chatbot handles customer queries about transactions, providing quick and convenient support.
For those looking to implement AI chatbots, here are some actionable tips: Start by addressing the most common customer inquiries, ensuring a quick win and demonstrating value. Ensure a seamless handoff to human agents when the chatbot encounters complex issues, maintaining a positive customer experience. Continuously train the AI with real conversation data to improve accuracy and effectiveness. Regularly evaluate customer satisfaction with the chatbot to identify areas for improvement. Finally, make the bot's limitations clear to customers to manage expectations.
Popular platforms for building customer service AI chatbots include IBM Watson Assistant, Google's Dialogflow, Microsoft Bot Framework, and Amazon Lex. These platforms offer robust tools and resources to develop, deploy, and manage AI-powered chatbots. For non-technical AI enthusiasts, hobbyist vibe builders, and those interested in AI use cases, go-to-market strategies, AI workflow automations, prompting LLMs, and integrations with platforms like Replit, n8n, and Zapier, exploring these chatbot solutions can unlock a new level of customer engagement and operational efficiency.
2. Predictive Analytics for Business Forecasting
Predictive analytics is a powerful AI-driven tool that empowers businesses to peer into the future. By analyzing historical data, identifying patterns, and leveraging machine learning algorithms, predictive analytics forecasts various business outcomes. This includes crucial aspects like sales trends, inventory needs, customer behavior, and even broader market changes. Instead of relying on gut feelings or outdated methods, predictive analytics lets you make data-driven decisions and create more strategic, forward-thinking plans. It's a prime example of AI in business examples, offering a tangible way to improve efficiency and gain a competitive edge.
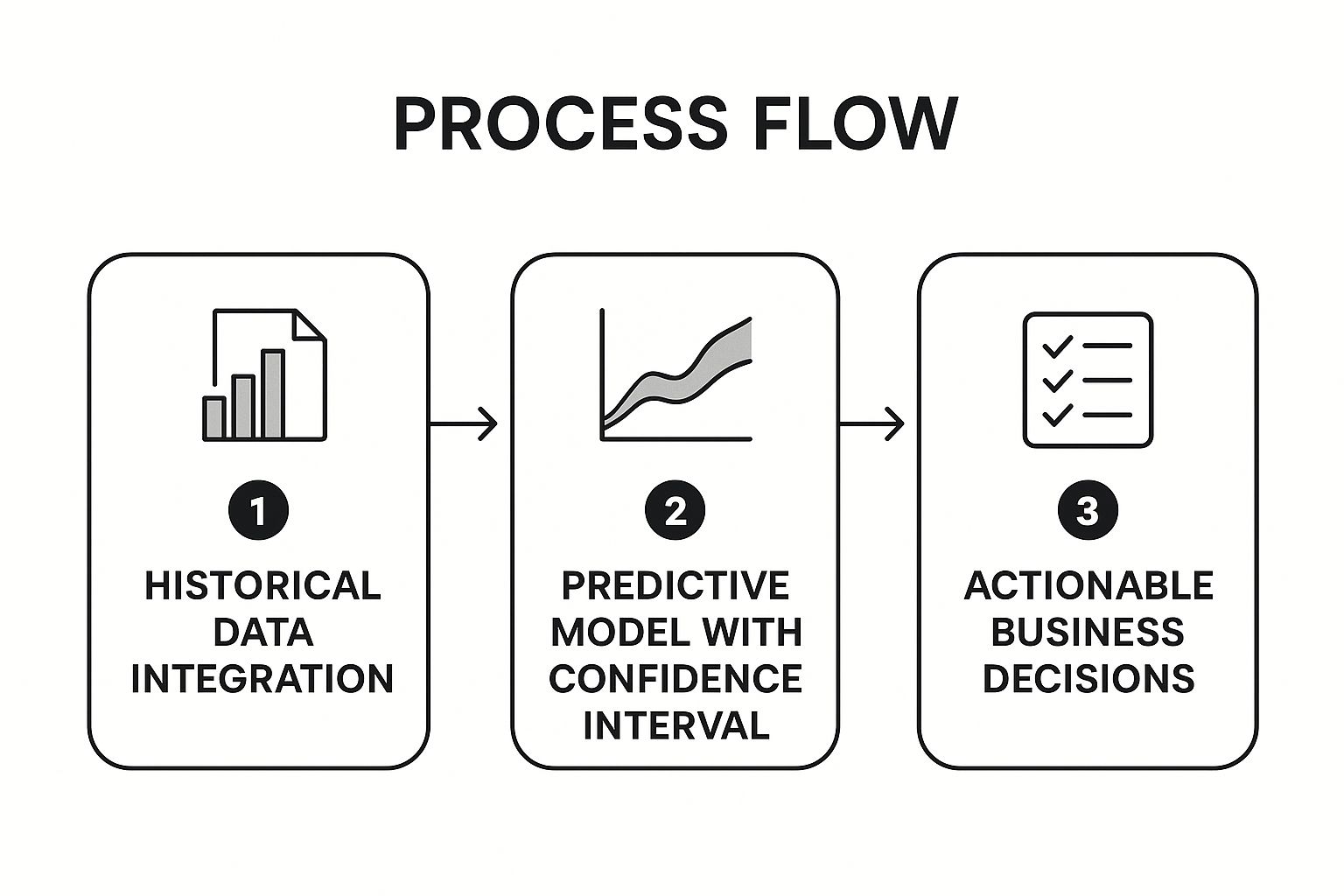
The infographic above illustrates the process flow of predictive analytics for business forecasting. It starts with defining the business objective, then moves to data collection and preparation. The core of the process is the development and deployment of a predictive model, followed by ongoing monitoring and refinement. Finally, the insights gained are used to make data-driven decisions. The cyclical nature of the diagram highlights the importance of continuous improvement and adaptation in predictive analytics. The clear visualization of the steps involved emphasizes the structured and iterative nature of building a successful forecasting model.
Features like machine learning algorithms for pattern recognition, the ability to integrate multiple data sources, automated forecasting with confidence intervals, real-time data processing, scenario analysis, and visualization tools make predictive analytics a robust solution. Imagine being able to explore "what-if" scenarios and present your insights with compelling visuals!
This approach deserves a spot on this list because it's a practical and widely applicable AI solution. Whether you're a hobbyist vibe builder looking to understand audience engagement, or a business exploring go-to-market strategies, predictive analytics can offer valuable foresight. It's especially relevant for those interested in AI workflow automation, as it can be integrated into various platforms like Replit, n8n, and Zapier.
Pros:
- Improves forecast accuracy by 15-30% compared to traditional methods.
- Enables proactive decision-making.
- Optimizes inventory and resource management.
- Identifies market opportunities and risks earlier.
- Reduces operational costs through better planning.
Cons:
- Requires clean, comprehensive historical data.
- Can be expensive to implement and maintain.
- May require specialized staff or training.
- Results can be difficult to interpret without a data science background.
- Model drift requires regular updating.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Walmart: Uses predictive analytics to optimize inventory across thousands of stores, ensuring the right products are available at the right time.
- Amazon: Employs a sophisticated demand forecasting system to manage its massive inventory and anticipate customer needs.
- Starbucks: Predicts customer preferences and uses this data to inform decisions about new store locations.
- UPS: Optimizes delivery routes and staffing using predictive models, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Tips for Implementing Predictive Analytics:
- Begin with clear business objectives for your forecasting. What exactly are you trying to predict?
- Ensure data quality before implementing predictive models. Garbage in, garbage out!
- Start with simpler models and increase complexity as needed. Don't overcomplicate things from the start.
- Combine AI insights with domain expertise for the best results. Human intuition still matters!
- Regularly validate predictions against actual outcomes. Continuous monitoring is key.
Popularized by platforms like SAS Advanced Analytics, IBM SPSS, Salesforce Einstein Analytics, and SAP Predictive Analytics, predictive analytics is becoming increasingly accessible.
Learn more about Predictive Analytics for Business Forecasting This link offers a great starting point for anyone interested in delving deeper into the topic. When and why should you use this approach? Consider it when you need to make data-driven decisions about the future, optimize resources, or gain a clearer understanding of trends and patterns. It's a valuable tool for any business or individual looking to leverage the power of AI for better planning and improved outcomes.
3. Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) represents a significant leap forward from basic Robotic Process Automation (RPA). While RPA excels at automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, IPA takes it further by incorporating artificial intelligence. This powerful combination allows businesses to automate complex processes that previously required human judgment, intuition, and decision-making. IPA works by mimicking human actions, like navigating software and manipulating data, but also by making intelligent decisions based on data analysis and learning. This ability to handle unstructured data, learn from exceptions, and continuously improve makes IPA a game-changer for businesses looking to optimize their operations and unlock new levels of efficiency.
IPA deserves a prominent spot on any list of AI in business examples because of its transformative potential. Features like process mining identify automation opportunities, while cognitive capabilities enable the processing of unstructured data like emails and documents. Decision engines, powered by machine learning algorithms, make intelligent choices, while adaptive workflows ensure the system evolves alongside the business. Natural language processing allows IPA to understand and extract information from documents, and seamless integration with legacy systems minimizes disruption during implementation. Think of it as having a digital workforce that can learn, adapt, and tirelessly execute complex processes.
Several impressive real-world successes demonstrate the power of IPA as an ai in business example. JP Morgan's COIN (Contract Intelligence) analyzes legal documents, saving an astounding 360,000 hours of manual work annually. Unilever automated supplier onboarding, slashing processing time from weeks to mere days. AXA leveraged IPA for claims processing, achieving a 40% reduction in handling time. Siemens automated invoice processing globally, realizing 80% straight-through processing.
Pros:
- Significant time savings: Reduces processing time by 50-90% for many tasks.
- Cost reduction: Decreases operational costs while simultaneously improving accuracy.
- Scalability: Scales operations without requiring proportional staff increases.
- Handles complexity: Manages variations and exceptions that basic RPA can't handle.
- Auditing: Creates detailed audit trails automatically.
Cons:
- Initial investment: Requires a significant upfront investment.
- Complex implementation: Needs specialized expertise for successful implementation.
- Change management: Can present challenges for the existing workforce.
- Security risks: Potential security vulnerabilities if not implemented and managed correctly.
- Maintenance: Requires ongoing maintenance and updates.
Tips for Implementing IPA:
- Start small: Begin with process analysis to pinpoint high-value automation candidates.
- Phased approach: Implement in phases rather than attempting a large-scale, enterprise-wide rollout.
- Incremental AI integration: Combine RPA with AI technologies incrementally to build complexity and capability over time.
- Center of Excellence: Establish a Center of Excellence to manage automation initiatives and best practices.
- Retraining: Invest in retraining affected employees for higher-value tasks, easing the transition and maximizing the benefits of IPA.
When and Why to Use IPA: Consider IPA if your business grapples with complex, time-consuming processes involving significant manual effort, especially those handling unstructured data like documents and emails. If you're looking to dramatically improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance accuracy, and free up your human workforce to focus on more strategic activities, IPA may be the perfect solution. Platforms like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism, and WorkFusion are popular choices for implementing IPA.
Learn more about Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) This link might offer additional resources for those interested in exploring no-code AI tools, which can complement and extend the power of IPA, particularly for non-technical users and hobbyist vibe builders looking to leverage ai in business examples.
4. AI-Powered Recruiting and HR
AI is revolutionizing how businesses manage their human capital. This section explores AI-powered recruiting and HR, a prime example of AI in business, showcasing how it streamlines processes, improves decision-making, and ultimately enhances the employee experience. These intelligent systems automate and optimize various HR functions, from candidate screening to employee development, making them more efficient and effective. This earns its spot on this list because it addresses a core business challenge: finding, retaining, and developing top talent.
How it Works:
AI-powered HR tools leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze vast datasets of candidate and employee information. This data can include resumes, job applications, performance reviews, and even social media activity (where applicable and ethical). By identifying patterns and insights within this data, AI can automate tasks, predict outcomes, and provide personalized recommendations.
Features and Benefits:
These systems offer a range of features designed to streamline HR operations:
- Resume parsing and intelligent screening: Automatically extracts key information from resumes and filters candidates based on pre-defined criteria, saving recruiters significant time.
- Candidate matching algorithms: Matches candidates to open positions based on skills, experience, and cultural fit, improving the quality of hires.
- Bias detection and mitigation: Identifies and flags potential biases in hiring processes, promoting fairer and more equitable outcomes.
- Predictive analytics for employee retention: Predicts which employees are likely to leave the company, allowing HR to intervene proactively.
- Automated interview scheduling and feedback collection: Streamlines the interview process and gathers feedback efficiently.
- Personalized learning and development recommendations: Provides tailored learning recommendations to employees based on their individual needs and career goals.
Pros:
- Reduces time-to-hire: By automating tasks like screening and scheduling, AI can significantly reduce time-to-hire, often by up to 70%, as seen with Unilever's implementation of HireVue.
- Improves quality of hires: Data-driven selection processes lead to better matches between candidates and roles.
- Decreases unconscious bias: AI can help identify and mitigate biases, promoting fairer hiring practices.
- Enhances employee engagement: Personalized learning and development opportunities foster a more engaging employee experience.
- Identifies flight risks: Predictive analytics can alert HR to potential attrition risks, allowing for timely intervention.
Cons:
- Potential for bias amplification: If not carefully designed and monitored, AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate existing biases.
- Privacy concerns: Handling sensitive employee data requires careful consideration of privacy regulations.
- Lack of human judgment: AI may struggle with nuanced situations that require human empathy and understanding.
- Integration challenges: Integrating AI tools with existing HR systems can be complex.
- Employee resistance: Transparency is key, as employees may resist AI-driven HR processes if they perceive them as intrusive surveillance.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Unilever: Uses HireVue's AI platform to screen entry-level candidates, reducing hiring time by 75%.
- IBM: Watson Career Coach provides personalized career advice and development recommendations to IBM employees.
- Hilton: Leverages AI recruiting tools to dramatically reduce time-to-hire from 42 days to just 5.
- Pymetrics: Helps companies like LinkedIn and Accenture match candidates to roles using neuroscience games and AI.
Actionable Tips:
- Combine AI with human judgment: Use AI recommendations as a starting point, but always involve human oversight for final decisions.
- Regularly audit for bias: Conduct ongoing audits to ensure AI systems are not perpetuating or amplifying biases.
- Transparency is key: Be open and honest with candidates and employees about how AI is being used in HR processes.
- Start small and focused: Begin with specific HR challenges rather than attempting a broad, all-encompassing implementation.
- Ensure compliance: Adhere to all relevant privacy regulations, such as GDPR.
Learn more about AI-Powered Recruiting and HR to explore the future of work and how AI is transforming HR strategies. This is especially important for our audience of non-technical AI enthusiasts, hobbyist vibe builders, and those interested in AI for go-to-market strategies, workflow automations, and prompting LLMs. Companies are actively exploring AI tools like those provided by HireVue, Pymetrics, Textio, and Eightfold AI to optimize their HR functions, and understanding these trends is crucial for staying ahead of the curve.
5. AI for Personalized Marketing
AI for personalized marketing represents a powerful application of AI in business, transforming how companies interact with their customers. This approach leverages AI systems to analyze vast amounts of customer data, enabling businesses to deliver highly personalized marketing experiences across various channels. These AI-powered tools can predict customer preferences, optimize the timing of content delivery, personalize messaging, and continually improve campaign performance through machine learning. This means no more generic email blasts; instead, customers receive tailored content and offers that resonate with their individual needs and interests. This makes AI-driven personalized marketing a prime example of AI in business examples, deserving of its spot on this list.

Features like dynamic content generation, customer segmentation using clustering algorithms, predictive customer lifetime value modeling, next-best-action recommendations, multi-channel optimization, and real-time personalization based on behavior make this a highly sophisticated and effective marketing strategy. Imagine creating unique vibes for each customer segment! This is particularly relevant for vibe builders and those exploring AI for go-to-market strategies. By understanding individual customer journeys, AI can help automate workflows (think Zapier, n8n, or Replit use cases) and even assist in prompting LLMs for personalized content creation.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Netflix: Their recommendation engine drives 80% of content consumption through personalized suggestions.
- Spotify: Discover Weekly creates personalized playlists for millions of users, enhancing their music discovery experience.
- Amazon: Their product recommendation engine is a powerhouse, driving 35% of total sales.
- Sephora: Offers personalized beauty recommendations based on customer profiles and purchase history, creating a more tailored shopping experience.
Pros:
- Increased Conversion Rates: Expect a 10-30% boost through relevant targeting.
- Improved Customer Experience: Personalized interactions foster stronger customer relationships.
- Optimized Marketing Spend: Focus resources on high-value segments for maximum ROI.
- 1:1 Marketing at Scale: AI makes personalized marketing feasible even for large customer bases.
- Deeper Customer Insights: Gain valuable data to inform product development and refine marketing strategies.
Cons:
- Privacy Concerns: Requires significant customer data, raising potential privacy issues.
- Intrusiveness: Overly aggressive personalization can be perceived negatively.
- Data Maintenance: Requires continuous data collection and model updates.
- Integration Challenges: Connecting AI tools with existing marketing platforms can be complex.
- Initial Investment: Comprehensive implementation can require a significant upfront investment.
Tips for Implementation:
- Data Strategy: Start with a clear data strategy before implementing AI marketing tools.
- Privacy Balance: Carefully balance personalization with privacy considerations to build trust.
- A/B Testing: Test AI recommendations against control groups to measure their impact accurately.
- Human Expertise: Combine AI insights with marketing expertise for optimal results.
- Gradual Rollout: Build personalization gradually to avoid overwhelming customers.
When and why should you use this approach? If you're looking to boost customer engagement, improve conversion rates, and optimize your marketing spend, AI-powered personalization is a game-changer. It allows you to connect with your audience on a deeper level, fostering loyalty and driving business growth. For non-technical AI enthusiasts and hobbyist vibe builders, understanding these applications is crucial. Learn more about AI for Personalized Marketing to explore how AI is revolutionizing the creative industries. Platforms like Adobe Experience Cloud, Salesforce Marketing Cloud, Persado, and Dynamic Yield (acquired by McDonald's) have popularized these powerful tools, making them increasingly accessible to businesses of all sizes.
6. AI-Powered Financial Analysis and Fraud Detection
AI is revolutionizing the financial industry, offering powerful tools to analyze massive datasets and uncover hidden insights far beyond human capability. This makes AI-powered financial analysis and fraud detection a prime example of AI in business. These systems ingest financial transactions, market data, and customer behavior to detect fraudulent activities, assess credit risk, optimize investment strategies, and provide a wealth of other financial insights. Think of it as having a tireless digital detective constantly watching over your finances.
How it Works:
These AI systems utilize a variety of techniques including:
- Real-time Transaction Monitoring and Scoring: Every transaction is analyzed instantly, assigning a risk score based on various factors. This allows for immediate flagging of suspicious activity.
- Anomaly Detection using Unsupervised Learning: AI algorithms learn to identify unusual patterns and deviations from the norm without explicit instructions, effectively uncovering hidden fraud and emerging risks.
- Predictive Risk Modeling: AI anticipates potential future risks by analyzing historical data and current trends, enabling proactive risk mitigation strategies.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Financial Document Analysis: AI can process and understand complex financial documents, automating tasks like contract review and due diligence.
- Network Analysis to Identify Fraud Rings: AI can map relationships between individuals and entities to uncover sophisticated fraud rings and organized criminal activity.
- Behavioral Biometrics for Authentication: AI analyzes typing patterns, mouse movements, and other behavioral traits to enhance security and prevent unauthorized access.
Successful Implementations:
Several financial giants are already leveraging the power of AI:
- Mastercard's Decision Intelligence: Analyzes over 2 billion cards for fraud protection in real-time.
- JPMorgan Chase: Uses AI for document processing, reportedly saving 360,000 hours of manual work annually.
- PayPal: Utilizes deep learning to distinguish between legitimate and fraudulent transactions with remarkable accuracy.
- American Express: Employs AI models to increase fraud detection rates while simultaneously reducing false declines, improving the customer experience.
Why Use AI-Powered Financial Analysis and Fraud Detection?
This approach is essential for any business dealing with financial transactions because:
- Improved Accuracy: AI reduces false positives in fraud detection by up to 80% and improves credit risk assessment accuracy significantly.
- Enhanced Security: It identifies complex fraud patterns that traditional rule-based systems often miss, providing a robust layer of security.
- Increased Efficiency: Automates tedious tasks like document processing and transaction monitoring, freeing up human resources for more strategic activities.
- Cost Reduction: Streamlines operations and reduces manual labor, ultimately lowering operational costs.
Pros & Cons:
Pros:
- Reduced false positives in fraud detection
- Identifies complex fraud patterns
- Improves credit risk assessment
- Faster transaction processing with better security
- Reduced operational costs
Cons:
- High implementation costs for sophisticated systems
- Requires ongoing model training and tuning
- "Black box" nature can make regulatory compliance challenging
- Requires large, clean datasets for effective training
- Potential for algorithmic bias in lending decisions
Actionable Tips:
- Combine rules-based and AI approaches: This creates a robust and comprehensive fraud detection system.
- Ensure transparency in financial AI systems: This helps with regulatory compliance and builds trust.
- Regularly retrain models: Keeps the system up-to-date with evolving fraud tactics.
- Create human-in-the-loop systems for high-risk decisions: Provides crucial human oversight for critical decisions.
- Thorough testing before deployment: Avoids negative impacts on customers and operations.
Popularized By:
- FICO Falcon Fraud Manager
- Feedzai
- Darktrace
- Kount (acquired by Equifax)
This AI-powered approach deserves a place on this list because it offers a tangible and powerful way for businesses to enhance their financial security, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in today's rapidly evolving financial landscape. For hobbyist vibe builders and those exploring AI use cases for go-to-market strategies, the potential of automating workflows and prompting LLMs for financial insights opens exciting new possibilities. While implementation can be complex, the benefits are compelling and make it a worthwhile exploration for many businesses.
7. Computer Vision for Quality Control: The AI-Powered Inspector
Computer vision for quality control is a powerful example of AI in business, transforming how companies ensure the quality of their products. This technology leverages cameras and deep learning algorithms to automate visual inspections, detecting defects often invisible to the human eye, and doing so with greater speed and consistency. Imagine a tireless inspector who can work 24/7, spotting microscopic flaws on a fast-moving production line – that's essentially what computer vision delivers. This makes it a game-changer for industries ranging from manufacturing and automotive to food processing and electronics.
How it Works:
At its core, computer vision for quality control involves training an AI model on a vast dataset of images representing both acceptable and defective products. This training process allows the AI to learn the subtle visual cues that indicate a flaw. During operation, high-resolution cameras capture images of products on the production line. These images are then processed by the trained AI model, which identifies and classifies any defects in real-time. The system can even be integrated with production control systems to automatically trigger actions, such as removing a flawed product from the line or adjusting machinery.
Features and Benefits:
- High-resolution image capture and processing: Captures intricate details often missed by human inspectors.
- Defect classification and categorization: Automatically categorizes defects based on type and severity.
- Real-time inspection on production lines: Provides immediate feedback for rapid intervention.
- Continuous learning from new defect patterns: The system improves its accuracy over time as it encounters new data.
- Integration with production control systems: Enables automated responses to quality issues.
- Thermal and multispectral imaging capabilities: Expands inspection capabilities beyond visible light, detecting temperature variations and other invisible anomalies.
Real-World Examples:
- BMW: Uses AI visual inspection systems to identify tiny scratches and dents in car bodies, ensuring flawless finishes.
- Foxconn: Reportedly replaced 60,000 factory workers with AI-powered quality control systems, demonstrating the potential for automation.
- Nvidia: Employs computer vision to inspect GPU chips for manufacturing defects, maintaining the high quality of its products.
- Unilever: Implemented computer vision in food processing for consistent quality control, ensuring product uniformity and safety.
Pros:
- Reduces defect escape rates by up to 90%: Significantly improves product quality and reduces costly recalls.
- Operates continuously without fatigue or variation: Ensures consistent inspection quality regardless of shift or workload.
- Inspects products at much higher speeds than human inspectors: Increases production throughput and efficiency.
- Creates detailed documentation of quality issues: Provides valuable data for process improvement.
- Scales easily across multiple production lines: Offers a cost-effective solution for large-scale quality control.
Cons:
- High initial investment in cameras and computing infrastructure: Requires significant upfront capital expenditure.
- Requires extensive training data of defects: Collecting and labeling training data can be time-consuming and expensive.
- May need regular recalibration for new products: Adapting the system to new product lines requires retraining.
- Environmental factors (lighting, vibration) can affect performance: Careful consideration of the production environment is crucial for optimal results.
- Installation may require production line modifications: Integrating the system into existing infrastructure may necessitate changes to the production line.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Start with high-impact, well-defined inspection tasks: Focus on specific areas where automated inspection will deliver the greatest value.
- Collect a comprehensive dataset of defects before implementation: Ensure the AI model is trained on a representative sample of potential defects.
- Ensure proper lighting and camera positioning for optimal results: The quality of the input images directly impacts the system's accuracy.
- Integrate with manufacturing execution systems for automated response: Enable seamless communication between the inspection system and production control systems.
- Train staff to interpret and act on AI inspection results: Empower your team to effectively utilize the data provided by the system.
Why Computer Vision Deserves a Spot on This List:
Computer vision for quality control is a prime example of AI in business because it addresses a critical challenge faced by countless companies: ensuring product quality. It offers tangible benefits in terms of reduced defects, increased efficiency, and improved consistency. This technology is rapidly becoming a must-have for businesses seeking to stay competitive in today's demanding market, making it a worthy addition to any list of AI in business examples. Popularized by companies like Cognex, Landing AI, Instrumental, and Neurala, this technology is readily accessible and offers a strong ROI for businesses willing to invest in it. This technology is perfect for hobbyist vibe builders, AI use cases, Vibe marketing, AI for go-to-market, AI workflow automations enthusiasts. While not directly related to prompting LLMs, Replit, n8n, or Zapier, its underlying principles of automation and data-driven decision-making resonate with these use cases.
7 AI Business Applications Comparison
| Solution | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Service AI Chatbots | Medium to High; requires NLP and integration | Medium to High; ongoing updates & training | Reduces costs by ~30%, provides 24/7 instant support | Customer support, ecommerce, multilingual support | Handles multiple inquiries simultaneously, improves consistency, collects insights |
| Predictive Analytics for Business Forecasting | Medium; requires clean data & ML expertise | High; data infrastructure & skilled staff | Forecast accuracy improved by 15-30%, cost reduction | Sales forecasting, inventory management, strategic planning | Enables proactive decisions, optimizes resources, identifies risks early |
| Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) | High; complex, needs specialized expertise | High; significant upfront investment & maintenance | Processing time cut by 50-90%, scales operations | Finance, insurance, healthcare, manufacturing | Automates complex tasks, handles exceptions, creates audit trails |
| AI-Powered Recruiting and HR | Medium; integrating AI with HR systems | Medium; plus continuous audits & updates | Time-to-hire reduced up to 70%, bias mitigation | Hiring, employee development, retention strategies | Improves hire quality, reduces bias, enhances engagement |
| AI for Personalized Marketing | Medium; needs data strategy & platform integration | Medium to High; requires continuous data collection | Conversion rates increased 10-30%, better targeting | Customer engagement, campaign optimization | Enables scalable 1:1 marketing, deeper customer insights |
| AI-Powered Financial Analysis and Fraud Detection | High; requires regulatory attention & expert staff | High; ongoing model training and data needs | Fraud false positives reduced by up to 80% | Fraud detection, credit risk assessment, investment | Identifies complex fraud, improves security, automates processes |
| Computer Vision for Quality Control | Medium to High; needs specialized hardware & data | High; cameras, computing power, training data | Defect escape rates reduced by up to 90% | Manufacturing, production quality assurance | Inspects faster & more accurately than humans, documents quality issues |
Embrace the AI Revolution: Supercharge Your Business
From AI-powered chatbots revolutionizing customer service to computer vision streamlining quality control, the examples explored in this article showcase the tangible benefits of integrating AI into your business strategy. The key takeaway is that AI isn't just a futuristic concept; it's a powerful tool available today to optimize operations, personalize customer interactions, and drive data-driven decision-making. Mastering these AI applications can empower your business to achieve greater efficiency, unlock new growth opportunities, and stay ahead of the curve. These AI in business examples offer a glimpse into what's possible, but the real power comes from adapting these technologies to your specific needs.
For those looking to streamline their development process and integrate AI solutions more effectively, explore the innovative approach of vibe coding (Source: What is vibe coding? Fast AI-Powered Development from Vibecoding VIP), which leverages AI to create software based on desired outcomes rather than line-by-line instructions. This can be a game-changer for implementing the AI solutions discussed here, like intelligent process automation or personalized marketing campaigns. By embracing these advancements, you're not just adopting technology; you're investing in a future where your business thrives in the age of AI.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of AI and connect with a community of like-minded innovators? Join VibeMakers, a platform designed to empower you with resources and connections to navigate the ever-evolving AI landscape and discover even more inspiring AI in business examples. Explore the future of AI, together.